The most popular gossip topic in the digital marketing world is “What is SEO Ranking Factors?”. We all do know that search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo etc uses nearly 200 ranking signals to index a page in SERP.
The Search Engine firms will never reveal the ranking factors implanted in their algorithms. But if you want your website to rank higher in the search result pages then you have to be knowledgeable about all Search Engine Ranking Factors.
The SEO requirements will be kept on changing and it’s very important to know about the latest changes in SEO. The various ranking signals which were used 2 years ago will not be applicable in current search engine algorithms.
Understanding the ranking signals used by the search engine is not as mysterious as it may seem. From many years people are trying to crack the search engine algorithms code and unravel the mystery of search engine ranking signals.
Complete List of 200 SEO Ranking Factors
Search Engine will use multiple algorithms to rank a web page in SERP and each algorithm will document the ranking signal which they are responsible.
In this article, I have mentioned all the latest search engine ranking signals. Some of them are demonstrated with proof, some are debatable and others are conjecture without firm evidence.
Here I categorized the more than 200 SEO Factors into 7 groups, namely:
- Web Page Ranking Signals
- Site Relevant Ranking Signals
- Keyword Ranking Signals
- Inbound Links Ranking Signals
- User Behaviour Ranking Signals
- Spammy Ranking Signals
- Algorithm Associated Ranking Signals
Web Page Ranking Signals
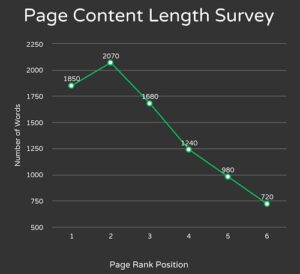
1. Content-Length: As we said in our ON Page SEO guide, search engine algorithm relies on site content. Web pages which have lengthy and descriptive content will send the clear indication to search engine that it has more concept and information related to searched query.
2. Table of Content: It helps both a search engine and user to clearly understand the topics explained in your page content. Linked table of content has a high probability to feature as the snippet.

3. Topic Coverage: The page headings which have an in-depth explanation of the topic will have more page authority than other sites which covers topic partially for similar heading.
4. Site Speed: Search engine measure the response time of your site. How quickly your website loads is an important SEO ranking factor used by both Google and Bing.
5. Score Code Composition: The way in which the site coding structure is organized and how fluently the search engine bots can crawl your site. Complexity in source code layout will hurt site ranking.
6. Browser Compatibility: The search engine will consider how efficiently your webpage will collaborate with a web browser. For same query search results will vary based on the browser used by the visitors.
7. AMP Pages: Mostly applicable for mobile SEO ranking factors and the pages with AMP links will rank higher in mobile or small gadgets search results.
8. Self Plagiarism: Using one’s own previously worked content in another context of the site can negatively influence search engine visibility.
9. Canonical Tag: Penalization for a web page having duplicate or similar content can be avoided with the use of canonical tags.
10. Optimized Images: Search engines will exploit the attributes of images which are a title, alt text, file name, caption and description as ranking factors of SEO.
11. Modification Date: The freshness of content is important for search engine, so the last modification date available in the sitemap will be used as one of the ranking signals.
12. Content Rephrase Magnitude: The update ratio on previous content and new content will be examined by the search engine algorithm. Adding or updating the entire section will be more significant than rephrasing few words or rearranging sentences.
13. Update Frequency: Search engine spiders will audit how often the page will be updated. Also, they will document and alter the page crawl frequency value as per site updating behaviour.
14. Outbound Links: Some SEO professionals believe that implanting links of highly authorized external sites with “do follow” attribute will be another relevancy ranking signal utilized by the search engine.
15. Grammar and Spelling: The pages which have proper grammar and spelling will tend to rank better in SERP and the quality signal of the site will be improved.
16. Plagiarised Content: The page rank will be influenced negatively if the content is copied or scraped from the indexed pages in SERP.
17. Hidden Content: One of the essential SEO Ranking Factor is when web pages which have text or links hidden from the user might not get indexed in the SERP.
18. Complementary Content: The additional or supplementary information which is indirectly relevant to page content is an indicator of page quality and usability. The supplementary content example includes reviews, filter option, related post, user comments.
19. Content in Accordion Tabs: Some SEO nerds speculate that forcing visitors to click the accordion tab element to view the content will weaken the ranking signal authority and will act as hidden content.
20. Dofollow Outbound Links: The ratio of inbound and outbound links will be monitored by the search engine. The site which has too many outbound links might hurt the page’s ranking.
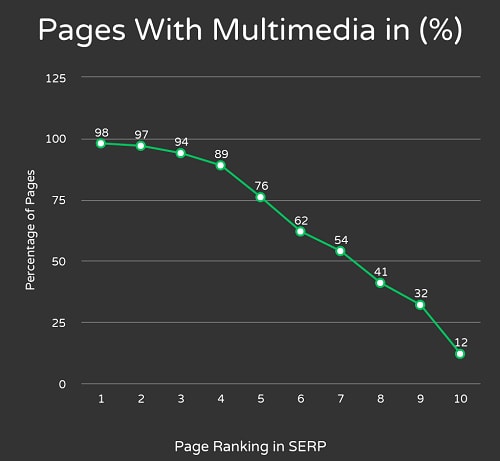
21. Multimedia: Videos, infographics, audio and other multimedia elements will act as quality signals in SEO ranking factors and enrich the page quality which improves ranking in SERP.
22. Deep Linking: The number of internal links on a page will improve the page quality and webpage content will be descriptive and understandable for both user and search engine.
23. The number of Internal Linked pages: The pages which are used many times for hyperlinking by other pages of your site will hold strong effect than other pages with less internal linked pages.
24. Quality of Internal Linked Pages: The authority of the linked page will benefit the linking page performance. Implanting the hyperlinks in pages which are performing well in SERP will boost the linked page rank in SERP.
25. Broken Links: The search engine will not appreciate page which has too many broken links. If the search engine bots find too many “404” error page links then will label the site as neglected or abandoned.
26. Readability Score: Some say site content reading level (basic, intermediate, advanced) will be analyzed by the search engine for ranking purpose. Content which is easy to read and understand will keep the user engaged and improve the time spent on site.
27. Affiliate Links: Search Engine prefer sites with original content which adds value for users. Sites which have thin relevant content and featuring the majority of page content from affiliate networks will suffer in search ranking.
28. URL Length: Extremely lengthy URL tends to have a minor disadvantage in page’s search engine visibility. In fact, several industry surveys reported that short URLs have a slight edge in the search engine result page.
29. Web Page Path: Complete path of the page in URL may get a slight boost in ON Page SEO ranking. URL path will interpret the site architecture and location of the page in the server.
30. Page Authority: Mostly pages with higher link metrics score will outperform the pages with fewer link metrics score in search results.
31. Page Taxonomy: The classification of pages into categories is a relevancy SEO ranking factor. Categorizing the pages will improve the site structure and may get a boost in ranking compared to a page which is not organized.
32. Tags: WordPress tags will improve your SEO score by relating one piece of content to another and quickly describe the crawlers what the page is about.
33. URL String: User-friendly URLs will deliver a positive effect on PageRank. Unorganized URL structure which contains special characters and numbers will affect the SEO of a webpage.
34. Source Reference: Citing authoritative references in the page content might be a quality ranking signal. Search engine quality guidelines state accurate information and trustworthy external source references can usually be rated as high-quality websites.
35. Video Content: The visibility of YouTube videos have a preferential impact on search results. Pages which incorporate video content will develop great visibility score for a wide range of keywords.
36. HTML Lists: Ordered and unordered HTML lists will make the content user-friendly and improve the readability score. Search engine bots are more likely to prefer content with HTML lists.
37. Sitemap Page Priority: The priority of page in XML sitemap will influence the crawl depth and SERPs ranking.
38. Keywords Ranking: If a page is ranking for multiple other keywords then it will trigger an internal quality ranking signal and might hike the rank of a primary keyword on search results.
39. Page Age: Although search engines promote fresh content an older page where the content is frequently updated may outrun a newer page.
40. Layout Design: Page layout is a building block of the website. Search engines go for high-quality user-friendly layout which makes the page content easy to use and understand.
41. Useful Content: Search engine differentiates between quality content and useful content. Pages having accurate content which justify the searched query will be given higher priority in search engine result pages.
42. Hyperlink Anchor: The internal link anchor text is a relevancy signal in the page content. Anchor text of hyperlinks will carry some ranking signal weight and it plays a vital role in SERPs ranking.
43. Schema Data: Pages which support Microformats (small pattern of HTML code which published content like people, event, location, site links, rating and reviews etc.) in the search results may gain an efficient boost in ranking.
Site Relevant Ranking Signals
44. Domain Validity: There has been widespread speculation that search engine use domain expiration date as a ranking signal. There is no evidence exist that prove these phenomena.
45. Age of Domain: For how long you have been constantly providing services on a particular field will be considered by the search engine. Domain age is an essential Google ranking factor but it’s not very important.
46. Domain History: Search engine analysis how your site (domain) behaved in the past. If you purchased a domain which has been penalized then you will carry documented penalty along with it.
47. Website Whois Credentials: Public and Private Whois information will be taken into consideration by the search engine. When domain “whois” privacy is on then the search engine may sense you are hiding something.
48. ccTLD Extension: Site having a country code Top Level Domain (.us, .in, .uk) will perform well in SERP for that particular country but they do have a hard time to rank globally.
49. W3C Standards: Too many HTML errors may send poor website quality signal to search engine. A website needs to be built in accordance with Wide Web Consortium validation to achieve better results in SEO.
50. Domain Authority: The site with higher domain authority score will rank better in SERPs than the domain which has less domain authority score.
51. Parked Website: The domains which are parked and haven’t done any modification from a long time will lose the search visibility.
52. Affiliate Sites: Search engine advise us to create websites with original content that adds value for the online audience. The websites which feature mostly content from affiliate programs will suffer in SERPs ranking.
53. Contact Credential: Some SEO nerds believe that search engine bots prefer sites which has a convenient amount of contact information. Make sure that your site contact details match domain registration credentials.
54. Trust Score: Search results ranking guidelines states that website TrustRank is a massively important SEO Ranking Factor. Trust factors are used to generate information retrieval scores of the webpage and search results are ranked based on the retrieved trust scores.
55. Website Architecture: Optimizing the website design and structure for SEO is essential. Ideally constructed website helps web SpiderBot to systematically crawl and index all the site’s pages.
56. Site Freshness: Some SEO professionals believe that producing new content frequently will improve the sitewide freshness factor. But search engine ranking algorithm analyst states publishing new pages per day doesn’t impact the ranking on SERP.
57. XML Sitemap: Search engine read the sitemap to intelligently crawl the website. An XML sitemap tells the web spider which pages are important, how often the page is changed and when the page was last updated.
58. Site Downtime: Occurrence of too many downtimes from website maintenance or server error will hurt the SEO rank and also may result in deindexing from result pages.
59. IP Location: Especially for geo-targeting search queries the location of the hosting server influences the site ranking in different geographical regions.
60. HTTPS Encryption: Security is a top level priority in SEO ranking factors. Implanting Secure Sockets Layer – SSL certification on the website will enhance the site ranking strength.
61. Privacy and Terms of Use Pages: Some speculate that these two pages uplift strong emphasis on authority, expertise and trustworthiness of a website.
62. Duplicate Title and Description: Every page should have the distinct title and description and duplication of meta information will bring down the visibility of pages in search results.
63. Breadcrumb: Navigation breadcrumb is a user-friendly site architecture which guide site audience and search engine bots know where they are located in the site hierarchy.
64. Responsiveness: More than half of searches are done from small screen gadgets and your website need to be adaptable for all devices. The site may get de-indexed if the responsiveness of webpage is not optimized.
65. Usability: The website which is not user-friendly and difficult to access will indirectly hurt SEO score through time user spent on site, pages viewed, scroll depth, bounce rate and exit rate ratio.
66. Web Analytics and Webmaster Tool: Some speculate that having these two tools setup on your site can improve site ranking and page’s indexing. Although web analytics and search console tool will collect more data about the website (i.e. site audience, traffic source, user behaviour, coverage, performance, site links etc.) so consequently they may impact the ranking on search engine result pages.
67. Online Reputation: Site reputation is an internal part of SEO ranking signals. User’s review and brand rating in the digital world will be utilized by a search engine ranking algorithm to provide better user experience in search results.
68. Brand Search: When people search website name in the search box will indicate search engines that the searched domain is a real brand.
69. Facebook Page: Site with official Facebook Page and the number of likes the page have will influence the SERP ranking.
70. Twitter Profile: Website having Twitter profiles with a lot of followers will signals brand popularity and may impact search results.
71. LinkedIn Page: Official company page on LinkedIn will improve the authenticity of the site.
72. Authentic Site: Within search engine result pages, information tied to verified online websites will be ranked higher than websites without such verification.
73. Genuine Social Media Accounts: Search engines implemented various methods and systems for detecting fake accounts in online social networks. Sites with a genuine audience with lots of interactions will be interpreted differently by the search algorithms.
74. NEWS Domains: Sites which compiles online news publisher policies and guidelines will get a ranking boost for trending keywords and also reserves a position in the top stories results panel.
75. Unlinked Brand: Domain name getting mentioned in the content without any hyperlink pointing at it will also indirectly acts as a brand quality signal.
76. MyBusiness Profile: Brick-and-Mortar location of the business will help search engine to validate site brand authenticity. Along with that customer reviews and ratings on a business profile will play a major role in site overall SERP ranking.
Keyword Ranking Signals
77. Keyword in URL: When you have a targeted keyword / searched query in the URL, it acts as a relevant ranking signal and will express the content of a webpage. Having the keyword in the URL will improve the search visibility of the website.
78. Keyword Position in the URL: The page which has targeted keyword right after the domain name will have an advantage over sites that have the keyword in the middle or end of the URL.
79. Keyword in Subdomain: Having a primary keyword as a subdomain name can boost ranking for relevant pages published underneath it. When you analyze closely, a bunch of boon and bane of subdomain can be identified.
80. Keyword Domain: Having targeted keyword as domain name [ Exact Matching Domain ] will give you a slight edge in SERP. As per the latest EMD update, Google will reduce low quality “Exact Match Domain” from the search result.
81. Keyword in Title Tag: Page title having targeted keyword will improve your SEO ranking factors score. Having a primary keyword in the title tag will increase website CRT [click through rate.
82. Keyword Position in Title Tag: Having primary keyword at the start of the title tag will slightly perform better in SERP than web pages which have the keyword at the end in the title tag.
83. Keyword in Meta Description: Search Engine can alter the page description based on the searched query and content relevancy in the webpage. Although it’s better to have targeted keyword in your default meta description to increase CRT.
84. Keyword in H1 Tag: H1 Tag describes the primary heading of web page content. On your landing page, first thing both user and search engine notice is H1 tag. Having targeted keyword in H1 tag will improve site visibility on search result pages.
85. TF-IDF: Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency is a numerical statistics used by a search engine for analysing website relevance with a user query.
86. Keyword Density: Search engine check “How often does a certain word appear in the article?” to determine the topic of the webpage. The site having high keyword density will be penalized by the search engine spam checker algorithm.
87. LSI Keyword: Latent Semantic Indexing Keywords helps site users and search engine spiders to understand the webpage content clearly. The presence of LSI keywords will improve the webpage content quality score.
88. LSI Keyword in Title and Description: The relevance of webpage content with targeted keywords will increase when you include LSI keywords in the title and description tag.
89. Keyword Prominence: Making the keyword noticeable by having the targeted keyword in the first paragraph of page content is considered a relevant ranking signal.
90. Keywords in Subheading: Pages which have the targeted keywords in subheading with H2, H3 … H6 tags will help search engine to understand the page structure and acts as relevant SEO ranking factors.
91. Entity Keyword Match: The page content which matches the exact query or an entity associated with multiple queries that the user is searching for..? may get a boost in ranking for that particular keyword.
Inbound Links Ranking Signals
92. Linking Domain Age: Backlinks from websites which is existing from a long time will be more effective than new websites.
93. Referring Domains: The number of linking domains is one of the popular ranking factors in OFF Page SEO. Sites having backlinks from multiple root domains have a strong influence on ranking than sites getting backlinks from the same domains.
94. C-Class Subnet Link: SEO community survey report suggested having links from different C-Class IP addresses will dramatically boost the power of your inbound links.
95. Linking Pages: The total number of inbound links a site has from the same domain will be examined by the search engine for ranking pages in search results.
96. Inbound Link Anchor: Generally inbound link anchor text provides a more factual description of website pages then the page themselves. Keyword rich anchor text will deliver strong relevance signal to web SpiderBot, although heavily optimized anchor tags will trigger the webspam signal.
97. Image Backlink: Web crawlers exploit image alt text as anchor text to understand the relevance between the image and linking page.
98. Backlinks from .gov or .edu domain: Few hypothesize that inbound links from a domain with .edu or .gov TLD extension have a special place in the ranking algorithm. Only universities and government organizations were able to get hands on these TLDs, thus backlinks from these domains were considered more valuable.
99. Referring Domain Authority: The domain authority of the linking page is an extremely important SEO ranking signal. The backlinks from good authority domains will benefit the PageRank of a site.
100. Linking Page Authority: The authority of the referring page is associated with the backlink metric score of a page. An inbound link from a page which is performing great in SERP will benefit the other linking pages.
101. Link From Opponent: Inbound link from a competitor page ranking in the same search results will be more beneficial for that appropriate keyword.
102. Expertise Site Backlink: Search engines can differentiate the website relevant industry and getting a backlink from websites who are expertise in your field of work will be more valuable.
103. Link From Atrocious Sites: Inbound links from the website which practices spammy or black hat strategies for ranking pages will be harmful.
104. Guest Author Link: Inbound links from guest posting will carry value but not as powerful as natural links. Although, a vast number of guest author backlinks may hurt overall website ranking.
105. Advertisement Link: Followed Backlinks from Ads will pass link juice and they likely aren’t as strong as true editorial links.
106. Backlink From HomePage: Links from a domain homepage may have special priority in ranking algorithm while evaluating referring page weight and authority.
107. Nofollow Backlink: Generally web crawlers don’t examine the “no-follow links” but some experts suggest that they do in certain cases. Having a few percentages of no-follow backlinks will balance the site’s link building approach.
108. Inbound Link Type: Having a large chunk of links from a single source (i.e. web forums, directory listing, comments) will hurt the page ranking and may result in webspam. In SEO ranking factors, diversity of inbound links type will enhance the backlink profile of a site.
109. Promotional Backlink: Inbound link from partner sites or sponsors link to increase sales and awareness may decrease the PageRank score of linking pages.
110. Contextual Link: Backlinks implanted inside the page content are accounted as more powerful than links embedded on other sections of the web page.
111. Redirection Link: As per Google SEO ranking guidelines, backlinks will 301 redirection status will weaken the link authority value.
112. Link Title Attribute: The title attribute in an anchor tag (the text which appears when we hover over the link) may be utilized as a thin relevancy signal.
113. Linking Domain TLD: Having inbound links from country specific TLD (Top Level Domain) extension (i.e .us, .in, .uk, etc.) may help linking pages to rank better in those countries.
114. Link Position in Content: Getting inbound links in the first 100 words of content transfer slightly more ranking weight than links appearing at the end of the page content.
115. Position of Link on Page: Location of link appearing on a page will be analyzed by search engine bots. Inbound links implanted in footer and sidebar widget is less powerful than links embedded in the page content.
116. Referring Domain Relevance: Backlink from a website which is similar to linking page niche is more valuable than a link from an unrelated site.
117. Referring Page Relevance: Backlink from a page which is relevant to linking page topic which improves the link metric weight and PageRank.
118. Keyword in URL and Title: Search Engine appreciate backlinks from pages that contain linking page targeted keyword in its URL and title tag.
119. Backlink Growth Velocity: Ranking algorithms evaluate the growth of site inbound links. Risk in backlinks velocity will boost the comprehensive ranking of website pages in SERPs.
120. The Decline in Backlinks: Drastic downturn in inbound link numbers may significantly affect the overall ranking of a site.
121. Non-Affiliated Pages: External links in pages that are authored by people from a non-affiliated organization are ranked well in search results. In theory, the search engine finds top resources which are usually considered as professional work and the pages that they like to will have a good chance in SERP.
122. Sovereignty Site Link: Backlink from authority sites which have good recognition in the online audience will pass more link juice than a link from the unpopular site.
123. Link from Wikipedia: Some SEO audit reports suggest that a backlink from Wikipedia source (even no-follow links) will drastically benefit the PageRank grade and will be an asset for a website.
124. Neighbouring Words: The phrases and text that surround the inbound link help crawlers to analyze what that page is about.
125. Inbound Link Age: Solid backlinks that have been around for a while and stay on the same place have more ranking capability than newly appeared links.
126. Link from Authenticate Sites: The search engine can easily distinguish between “Real Sites” and “Spam Blog Sites”. Due to rise in unethical link building techniques in blog networks, web crawlers may give more weight to links pointing from authenticating or branded sites than affiliate weblogs.
127. Natural Backlink: The webpage with a natural inbound link will rank higher in SERP than pages which implemented self-created backlink building strategies.
128. Reciprocal Link Exchange: Google ranking factors policy quoted “Excessive Link Exchanges” websites which practices cross-link exchange (you link to me and I’ll link to you) will negatively impact a page ranking in search results.
129. Link From UGC: Web spiders can distinct between online user-generated content and the content actually published by the website owner. For example, a backlink from a site similar to Quora, StackExchange or Jimbosite is very different from a backlink from Search Engine Laws portal.
130. Redirect Link: Inbound links which trigger 301 redirection status may lose a bit of link weight compared to direct links with 200 status signal code.
131. Linking Site TrustRank: The trust factor score of the referring site will impact the linked pages ranking on SERPs.
132. External Links on Page: Web Pages which contain lots of outbound links will contribute less towards PageRank than the pages which consist of a handful of external links.
133. Unnatural Backlink: The manipulated links in the forum sites and blog comment section may result in the violation of Google ranking factor guidelines.
134. Referring Page Word Count: Inbound link from a page which has 1000 words of content is more effective than a link from a page with have 200 words of content.
135. Content Quality of Linking Page: Backlink from poorly written or scraped content will not pass much value than a link pointing from well-written content.
136. Sitewide Backlinks: Search engine bots compress the sitewide links and consider it has a single backlink.
137. Branded Links: Inbound links which include the brand name in anchor text will benefit the site domain authority score.
138. PageRank Sculpting: Technique which distributes the link juice of the website to other linking pages which also include no-follow links. The search engine might prevent those links from getting PageRank that are not relevant to the referring page.
User Behaviour Ranking Signals
139. Click Through Rate: Pages which obtain more organic clicks will get a boost in SERP for that particular searched keyword.
140. Direct Search: Websites which get lots of direct search traffic will improve its ranking quality signal and also will get a boost in the search results.
141. Returned User: Web Pages which have a higher ratio of repeat traffic may get a ranking boost in SERPs.
142. Pogo Sticking: When the user scrolls the SERP results in an attempt to find the relevant answer to their query is referred to as Pogo Sticking. Pages which are skipped by a user in search results may notice the drop in ranking.
143. Blocked Website: Web browser allow users to add the site to their personal blocklist and search engines algorithm gather these data to improve user experience and help people find higher quality results.
144. Bookmarked Sites: SEO ranking score will enhance for pages that are bookmarked by users in their web browser and they might also get a rank boost.
145. Post Comments: Web page with lots of comments will trigger the signal of user interaction and help to outperform other pages in SERPs.
146. Time on Site: The search engine will monitor how long the user stayed on your page. This is also referred to as “Dwell Time” and the longer time spent by user, the better will be ranking.
147. Social Share: When people share the site post or page in their social profile then it will benefit the ranking of those pages in search results.
148. Bounce Rate: Not all SEO professionals agree that bounce rate matters in the ranking. Although some site audit report suggests pages with a higher bounce rate will not perform very for that particular keyword.
149. Exit Rate: SEO detectives conjectured that when people click on exit button after visiting your page via SERPs will specify that the user found what he has been looking for. Pages which got higher exit rate will get a ranking boost, whereas the pages where the user clicked on the back button and returned to search results will be influenced negatively.
50. Referral Traffic: Audience visiting the site from a source outside of search engine (such as email, notification, SMS, etc.) will have a good impact on website OFF Page SEO ranking signal.
151. Branded Search Query: When people search for a specific keyword along with the website name (keyword + brand) will indicate the search engine to categorize that domain as the brand. It may also help to achieve a ranking boost for “non-branded version” of that keyword.
152. Scroll Depth: Some conjectured that the depth of a page scrolled by the user will be utilized by the search engine to decide the rank in search results.
Spammy Ranking Signals
153. Penalized Owner: Few SEO nerds speculate that if search engine identifies a person or organization as a spammer, then it will examine and penalize other sites owned by them for spammy activities.
154. Content Farm: Site that employs the vast number of freelance writers to generate a large quantity of textual content and generate advertising revenue through attracting reader will be considered as spam content.
155. Bad Outbound Links: Referring out to spam web pages and sites having negative influence will hurt your search visibility.
156. Cloaking: Presenting distinct content or link to users and search bots is a violation of Google ranking factors. For example, serving a page of HTML text to web crawlers, while redirection users to a page of images or flash may cause a site to be penalized.
157. Distracting Popups: Pages with advertisements, popups or other features that distract or interrupt users from the use of the main content will be given a low rating.
158. Interstitial Ads: Website which utilizes full-screen ads that cover the user interface on their mobile phone and pressurize user into tapping on the ads will be de-indexing from search results.
159. Over Optimization: Site that optimizes pages more than necessary which include keyword stuffing, implanting targeted keyword in links, stuffing heading tags with keywords will hurt the page ranking in SERP.
160. Doorway Sites: Search engine penalize sites and pages which are created to rank higher for specific search queries. For example, having multiple domains or pages targeting specific cities or regions that redirect visitors to the targeted page without their knowledge.
161. Hidden Links: Pages that hide the links under images, background or alter the links to make it look similar as the textual format may get a spammy penalty.
162. Affiliate Content: Search engine prefers original content that adds value for visitors and sites that featuring mostly content which promote affiliate networks may suffer in search ranking.
163. Auto-generated Text: Content generated by an automation tool or through computer automated process, where text that makes no sense to the reader could result in de-indexing.
164. Spammed IP Address: All the websites hosted on the server will be affected if the server’s IP address is flagged as spam.
165. Meta Tag Stuffing: Sites can be hit with a penalty for stuffing keywords in the page title and description tags in an effort to rank higher in search engine result pages.
166. Malicious Sites: If your website hold pages which malicious code or gets hacked then the complete site will be deindexed from the search results. Although noopener and noreferrer tag protect the page to be accessed by the malicious sites.
167. Phoney Links: A massive influx of backlinks will increase the chances of site getting penalized.
168. Penguin Penalty: Search algorithm update with a codename “Google Penguin” designed to decrease search engine rankings of websites that breach webmaster guidelines by using black hat techniques for link building. Apparently, the penalty can be eliminated by submitting bad backlinks in the disavow tool.
169. Similar Source Links: Vast number of inbound links pointing from a common source (like forum sites and blog comments) may increase the odds of a site penalizing.
170. Irrelevant Backlinks: Lots of backlinks from sites that are not related to your site niche may increase the chances of a manual penalty.
171. Dodgy Links: Site owners will be notified with warning messages in webmaster tool if their site ranking is negatively influenced by low quality or potentially dangerous inbound links.
172. Business Listing: Backlinks from the low-quality bookmark sites or directory can lead to an overall site penalty.
173. Footer Spam: Widely distributed links in the site templates or footer is considered as an infraction of Google SEO ranking factors guidelines.
174. Widget Links: Auto-generated links (i.e hyperlinks which are not naturally placed) that are embedded in the widget section of the website may hurt the ranking of the website.
175. Same IP Class Links: Having a large number of backlinks from websites on the same Class C server IP address may help the search engine determine that the links are self-generated.
176. Poison Links: Hyperlinks that are planted throughout an entire website with same or identical anchor text could be the sign of spam and it will hurt the site’s SERPs ranking.
177. Backlink Spike: Search engine ranking algorithms can easily identify whether or not a hike across inbound links to a website or page is legitimate and links which shows the sign of perverse will be devalued.
178. Manual Action: Google will issue a manual action report in search console tool against websites when an official human validator has determined that the pages on the site are not following webmaster ranking guidelines.
179. Selling Links: Not only buying backlink will penalize a site, but also selling links may hurt the website search visibility in SERP.
180. Sandbox Effect: The competitiveness of the keywords used in links and an unusual influx of inbound links could cause sandbox effect, which temporarily holds the rank of pages to appropriately determine the page relevancy and also filter through the anti-spam mechanism.
181. Temporary Links: Search engines dranks the sites that spam the web with inbound links just to feed the ranking algorithms and remove them quickly to avoid penalty.
182. Disavow Process: Web pages which are victims of negative backlinks can manually remove the algorithm penalty through Disavow tools. Although unnecessary use of this feature can also affect the site ranking.
183. Reconsideration Request: Sites that are penalized can recover and may start appearing in the search results after successful approval of reconsideration request.
Algorithm Associated Ranking Signals
184. Mobilegeddon: It is a dub for mobile-friendly update algorithm. The responsiveness and reliability of the webpage on mobile devices is an essential Google ranking factor.
185. Hilltop Algorithm: The niche of the outbound linking page and the linked page content will act as relevance ranking signal. When the user enters a query in the search box, the hilltop algorithm will find results which are more informative about the keyword or query.
186. Human Crawler: Although never proven but some speculate that the search engine firm will assign human editors to influence the search results and ranking in SERPs.
187. RankBrain: RankBrain is Google’s ranking algorithm. SEO experts agree that search engines monitor how online audience interact with search results. The pages with user satisfaction answers will be ranked higher in the search results.
188. New Page Analysis: For certain keywords, the search engine will boost the newly indexed pages with the selected amount of users to understand how the user interact and respond with the webpage.
189. Keyword Diversity: When search query has lots of meaning associated with it then SERPs usually experience diverse results for ambiguous keywords.
190. Search History: User browsing history will be recorded in browser and sites which have been visited before by that user will get a rank boost.
191. Customized Results: Personalized search results will be presented that will prioritize the pages as per user previous queries. For example, if you search for “exam” then search for “cat” and you might get a page related to “common admission test”.
192. Snippets: Page HTML structure, authority, content and formatting will be utilized by the search engines to generate featured snippets results.
193. Geo Location: Research showed the correlation between server location and user geographic location will impact the results in SERP.
194. Safe Results: When the safe search is turned on then pages which have curse words or 18+ content will not appear in the search results.
195. YMYL Pages: The sites that solicit personal information, monetary transactions, medical information and which provide major life decision advice should maintain higher quality standards to rank for YMYL (Your Money Your Life) keywords.
196. DMCA Complaints: Websites which hold registered Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) complaint will downrank.
197. Bigfoot Update: The so-called “Google ranking algorithm update” which was focused on adding diverse domains to each SERP page.
198. Transactional Query: Pages with information that indicates an intent to complete a transaction, such as making a purchase will get a rank boost for transactional search queries.
199. Local Search: For location relevant keywords, the search engine often promotes results that allow people to connect face-to-face with a physical business.
200. Trending Topic: Certain trending keywords features the latest relevant pages in “Top Stories” search results panel.
201. Vince Update: Webmasters began noticing significant changes in ranking after the Google ranking factors algorithm update which gives big brands a major push in the search results.
202. Shopping Results: Sometimes sites that sell the product searched by people will be displayed in the sponsored shopping results panel.
203. Image Results: Specific user queries allow images to be displayed in organic search results.
204. Google Easter Eggs: Hidden features or messages can be found on search results for certain keywords. For example, if you search for “tic tac toe” or “Pacman” in the search box, then the playable game can be found on Google.
205. Single Domain Results: Single brand may dominate search results (where users can find a large number of results from a single site) for queries that indicate strong user interest in a particular domain.
206. Payday Loan Update: A special update in the ranking algorithm which specifically targets very spammy search queries.
207. Gibberish Pages: Content which is difficult to understand such as flow chart, textual diagram or foreign language will be filtered by a search engine. Using language model score and query stuffing score, a gibberish score will be generated which will determine or modify the ranking of gibberish content.
208. Page Layout Algorithm: Sites that don’t have much content “above the fold” and making users to scroll down the page past a slew of ads to see content may not rank well in search results.
209. Fred: Experts SEO analysis report documented an unconfirmed Google ranking update known by the name “Fred” that penalize sites which have low-quality content pages that focus only on generating revenue.
210. Rank Dance: Search engine ranking system can fluctuate page ranking for a limited amount of time to determine whether or not the page is relevant to the user search query.
Wrapping Up
That’s one heck of a list of search engine ranking factors which cover most of the major search engines like ( Google, Bing, Yahoo, Ask, DuckDuckGo ) ranking algorithm signals.
To summarize, here are the most important SEO ranking factors of this year:
- Page Content Quality and Length
- Quality Backlinks
- Domain Authority
- Responsiveness
- Meta Tags
- Dwell Time
- Page URL & Heading Tags
- Secure Site (HTTPS)
- Site HTML Structure
- OFF Site SEO Signals
Which SEO ranking from this list you think is important or took you by surprise.
Or have I missed any major Google 200 ranking signal?
Do let me know your thoughts in the comments below.

